Surgical Scissors A Comprehensive Guide by Hamsan Surgical
Introduction to Surgical Scissors
Surgical scissors are essential tools in any medical procedure, designed for precision cutting of tissues, sutures, and other materials. These instruments come in various shapes and sizes, each tailored to specific surgical needs. Hamsan Surgical, we recognize the critical role that high-quality surgical scissors play in ensuring successful outcomes in surgeries.
Historical Background
The use of cutting instruments in medicine dates back thousands of years. However, modern surgical scissors, as we know them, began to evolve in the 19th century with advancements in metallurgy and precision manufacturing. The first standardized surgical scissors were developed to meet the growing demands for accuracy and safety in surgery. Ref.[ Reiner Haag, Wilfried Storz- history from 1300 and 600 BC.]
Materials Used in Surgical Scissors
The choice of material in surgical scissors is crucial for their durability, performance, and ability to be sterilized. The most common materials include:
Stainless Steel
- Over 90% of surgical scissors are made from stainless steel due to its corrosion resistance and ease of sterilization.
Tungsten Carbide
- Often used for the cutting edges to provide enhanced durability.
- Scissors with tungsten carbide inserts last up to 20 times longer than standard stainless steel scissors.
Titanium
- Lightweight, strong, and non-magnetic, making it ideal for delicate surgeries.
- Titanium scissors are 50% lighter than their stainless steel counterparts, reducing hand fatigue during long procedures.
Design and Structure of Surgical Scissors
The design of surgical scissors varies depending on their intended use. Key design elements include.
Blade Types
- Sharp vs. Blunt: Sharp blades are used for precise cuts, while blunt blades are safer for handling delicate tissues.
- Curved vs. Straight: Curved blades provide better visibility and control in confined spaces, while straight blades offer precise, linear cuts.
- Fact: Curved scissors are preferred in 60% of surgeries that require intricate cuts.
Handle Types
- Ergonomic Designs: Modern scissors often feature ergonomic handles to reduce strain on surgeons during prolonged use.
- Fact: Ergonomically designed scissors can reduce hand strain by up to 30% compared to traditional designs.
Serrated vs. Non-serrated
- Serrated Blades: Provide a better grip on tissues, reducing the risk of slippage during cutting.
- Non-serrated Blades: Allow for smoother cuts but require more skill to handle effectively.
- Fact: Serrated scissors are commonly used in 40% of procedures involving dense or slippery tissues.
Specific Applications in Surgery
Surgical scissors are versatile tools used in various types of surgeries.
General Surgery
- Usage: Mayo and Metzenbaum scissors are commonly used for cutting tissues and sutures.
- Fact: Surgical scissors are used in nearly every general surgery, with a preference for those with curved blades for tissue dissection.
Cardiovascular Surgery
- Usage: Fine, sharp scissors are required for precise cutting of blood vessels and delicate tissues.
- Fact: Metzenbaum scissors are preferred in 65% of cardiovascular surgeries due to their precision.
Ophthalmic Surgery
- Usage: Iris scissors are crucial for delicate eye surgeries.
- Fact: Iris scissors are utilized in 85% of ophthalmic surgeries for their precision and control.
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Usage: Both sharp and blunt scissors are used to cut and shape tissues.
- Fact: Surgical scissors designed for plastic surgery are used in over 75% of reconstructive procedures.
Specialized Procedures
- Examples: Vascular scissors, dissecting scissors, and microsurgery scissors each serve specific roles in surgeries requiring specialized tools.
- Fact: Specialized surgical scissors are essential in over 60% of complex surgeries.
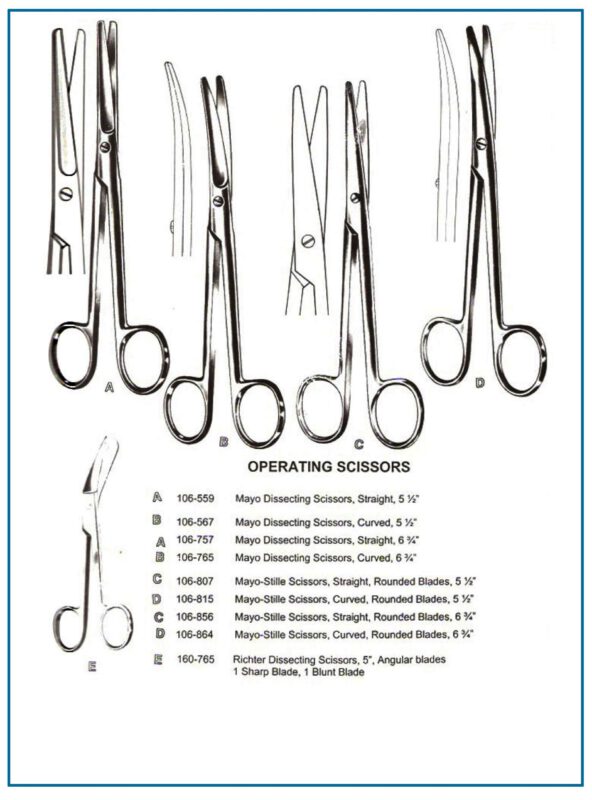
Types of Surgical Scissors
Different types of surgical scissors serve various functions in the operating room. Below are some of the most commonly used types:
Mayo Scissors
- Primarily used for cutting thick tissues, such as muscles and fascia.
- Available in both curved and straight forms, with a strong and durable build.
- Mayo scissors account for 35% of the cutting instruments used in general surgery.
General Surgery Set – 158 pcs
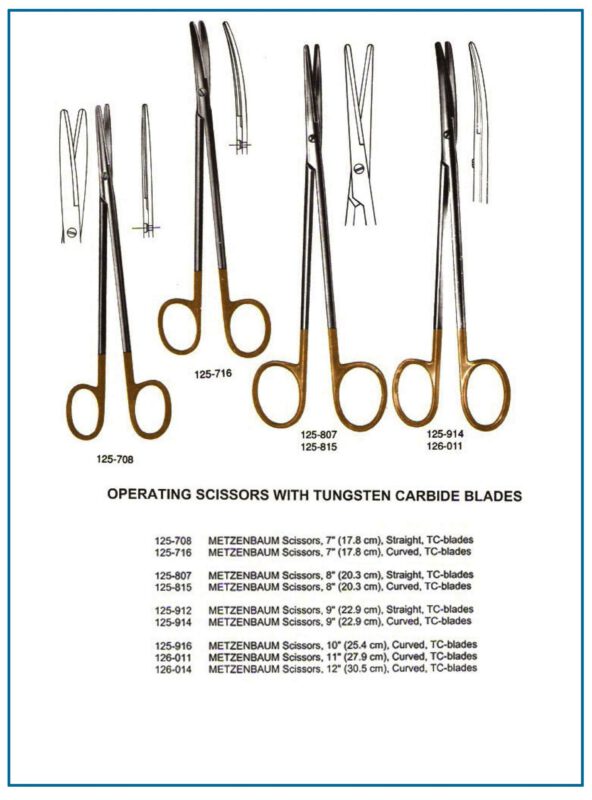
Metzenbaum Scissors
- Designed for cutting delicate tissues.
- Long handles with short blades, typically curved.
- Metzenbaum scissors are the go-to instrument in over 70% of soft tissue surgeries.
Basic Orthopedic Surgery Set
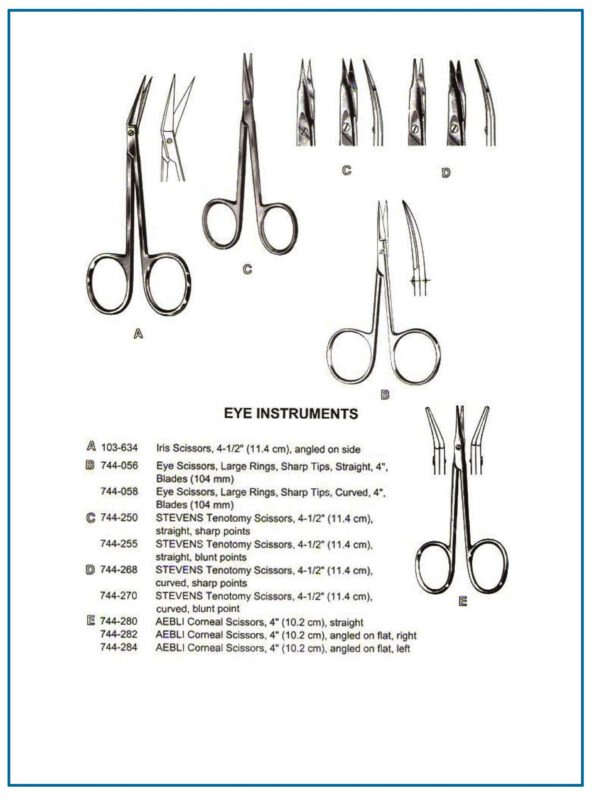
Iris Scissors
- Used in ophthalmic surgery for precise cutting.
- Small, sharp-pointed scissors, available in both straight and curved varieties.
- Iris scissors are preferred in 80% of microsurgeries due to their precision.
Gunter Rhinoplasty Surgery Set
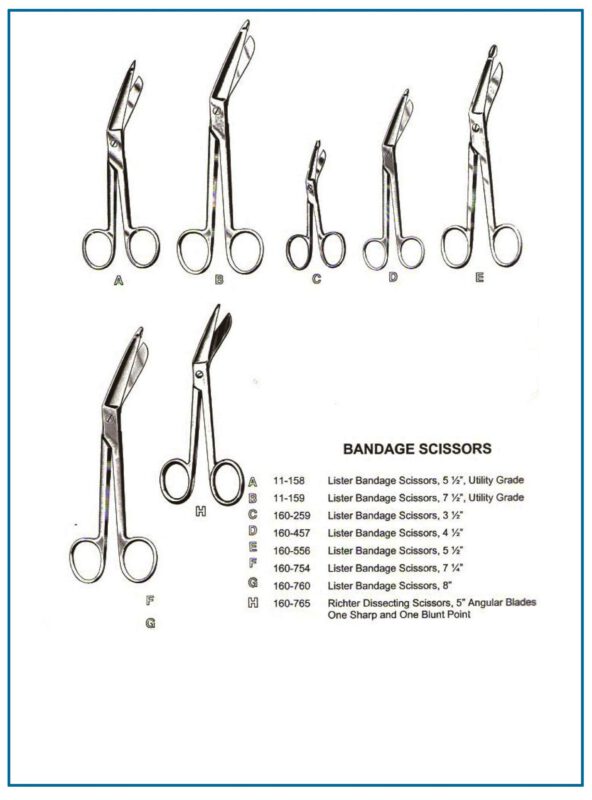
Bandage Scissors
- Used to safely remove bandages without damaging the skin.
- Angled blades with a blunt tip on the bottom blade to prevent injury.
- Bandage scissors are used in nearly every postoperative procedure.
Orthopedic Soft Tissue Surgical Set
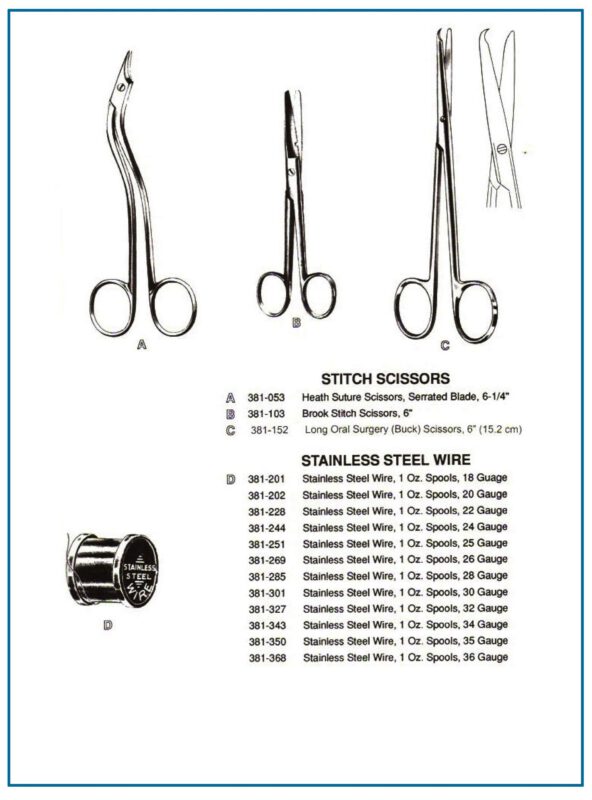
Suture Scissors
- Specifically designed for cutting sutures during surgery.
- Small, sharp scissors, often with a notch on one blade to hold the suture while cutting.
- Suture scissors are a staple in surgical kits worldwide.
Suture Instruments Set
How to Choose the Right Surgical Scissors
Selecting the appropriate surgical scissors depends on various factors:
Procedure Type
- Consideration: The nature of the surgery will determine the type of scissors needed. For instance, delicate surgeries require finer scissors like Metzenbaum or Iris scissors.
- Stat: Incorrect scissor selection can increase surgery time by up to 15%.
Material and Durability
- Consideration: For long-term use, tungsten carbide or titanium scissors are preferred due to their durability.
- Fact: Tungsten carbide scissors have a lifespan up to five times longer than standard stainless steel options.
Ergonomic Design
- Consideration: Ergonomically designed handles can reduce surgeon fatigue, especially in lengthy procedures.
- Fact: Scissors with ergonomic handles improve surgical precision by 20%.
Sterilization and Maintenance
Proper sterilization and maintenance of surgical scissors are crucial to their longevity and performance.
Cleaning Methods
- Importance: Regular cleaning is essential to remove blood, tissue, and other contaminants.
- Fact: 95% of surgical instruments, including scissors, are sterilized using autoclaves.
Sterilization Techniques
- Methods: Autoclaving, chemical sterilization, and ultrasonic cleaning are common methods.
- Stat: Autoclaving is used in 85% of surgical instrument sterilization processes.
Preventing Rust and Damage
- Tip: Regular lubrication and careful handling can prevent rust and prolong the life of the scissors.
- Fact: Surgical scissors made from stainless steel are resistant to rust but still require proper maintenance.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
- Advice: Inspect scissors regularly for signs of wear and tear. Sharpen blades when necessary, and replace them if they become dull or damaged.
- Fact: Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of surgical scissors by up to 50%.
Common Mistakes and Misuse
Using surgical scissors improperly can lead to complications:
Overuse or Wrong Use
- Risk: Using the wrong type of scissors for a specific procedure can damage tissues and prolong surgery time.
- Fact: Misuse of surgical scissors accounts for 10% of surgical complications.
Impact on Surgical Outcomes
- Consequence: Poor-quality or dull scissors can result in uneven cuts, leading to poor healing and increased infection risk.
- Stat: Proper scissor selection and maintenance can reduce postoperative complications by 25%.
Avoiding Damage to Tissue
- Tip: Always use the correct type of scissors for the tissue being cut to avoid unnecessary trauma.
- Fact: Sharp, well-maintained scissors reduce tissue damage in 90% of surgical procedures.
Innovations and Advancements
The field of surgical scissors has seen significant advancements:
Advanced Materials and Coatings
- Innovation: New materials like cobalt chrome and advanced coatings that enhance cutting performance and longevity.
- Fact: Scissors with advanced coatings have a 40% longer lifespan than traditional options.
Disposable vs. Reusable Scissors
- Trend: The use of disposable surgical scissors is increasing in certain procedures to reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
- Fact: Disposable scissors are becoming common in 30% of surgeries, particularly in high-risk environments.
Bandage Scissors Types
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
With proper care, surgical scissors can last for several years. Tungsten carbide scissors have a longer lifespan compared to stainless steel.
If scissors become dull, show signs of rust, or the blades are misaligned, it’s time to replace them.
Yes, surgical scissors can be sharpened by professionals to maintain their cutting efficiency.
Surgical scissors are designed for precision and are made from high-grade materials that can withstand sterilization. They are also sharper and more durable.
Always handle surgical scissors with care, using proper techniques to avoid injury. Ensure they are passed safely during procedures.
Yes, there are reusable surgical scissors and eco-friendly disposable options made from biodegradable materials.